The Legion Steps to Energy Calculator estimates what number of energy you burn primarily based in your peak, weight, variety of steps, common tempo, and the kind of strolling you probably did.
How the Legion Steps to Energy Calculator Works
To transform your steps to energy, the Legion Steps to Energy Calculator performs the next calculations:
Step 1: Estimate your stride size and the way far you walked.
The typical stride size is approximately 41.4% of an individual’s peak, which you’ll be able to estimate utilizing the equation:
- Stride size = peak (in meters) × 0.414
Utilizing this, the calculator determines how far you walked:
- Distance = stride size × steps
Step 2: Calculate strolling time.
To calculate the gap you walked, the Steps to Energy Calculator makes use of the next components:
- Time = distance ÷ velocity (in meters per second)
Step 3: Calculate energy burned.
Lastly, the calculator estimates the variety of energy you burned whereas strolling:
- Energy = time × METs × 3.5 × weight in kg/(200 × 60)
What Are METs?
You might have seen that the Legion Steps to Energy Calculator components in “METs”, and also you is perhaps questioning what they’re.
METs (Metabolic Equal of Activity) measure how a lot power an exercise burns in comparison with resting. A MET worth of 1 represents the energy burned whereas sitting nonetheless, whereas larger values point out larger power expenditure.
The Legion Steps to Energy Calculator MET values are primarily based on the kind of strolling you probably did and your velocity to supply an correct estimate of what number of energy you burned.
Listed below are the MET values the calculator makes use of for out of doors strolling:
- Very gradual (2.0 to 2.4 mph/3.2 to three.9 km/h) = 2.8 METs
- Sluggish (2.5 mph/4 km/h) = 3.0 METs
- Reasonable (2.8 to three.4 mph/4.5 to five.5 km/h) = 3.8 METs
- Brisk (3.5 to three.9 mph/5.6 to six.3 km/h) = 4.8 METs
- Very brisk (4.0 to 4.4 mph/6.4 to 7.1 km/h) = 5.5 METs
- Quick (4.5 to 4.9 mph/7.2 to 7.9 km/h) = 7.0 METs
- Very quick (5.0 to five.5 mph/8.8 to eight.9 km/h) = 8.5 METs
Listed below are the MET values for strolling on a treadmill:
- Very gradual (2.0 to 2.4 mph/3.2 to three.9 km/h) = 3.0 METs
- Sluggish (2.5 to 2.9 mph/4.0 to 4.7 km/h) = 3.5 METs
- Reasonable 3.0 to three.4 mph/4.8 to five.5 km/h) =3.8 METs
- Brisk (3.5 to three.9 mph/5.6 to six.3 km/h) = 4.8 METs
- Very brisk (4.0 to 4.4 mph/6.4 to 7.1 km/h) = 5.8 METs
- Quick (4.5 to 4.9 mph/7.2 to 7.9 km/h) = 6.8 METs
- Very quick (5.0 to five.5 mph/8.0 to eight.9 km/h) = 8.3 METs
And listed below are the MET values for Nordic strolling:
- Sluggish (2.5 to three.5 mph/4.0 to five.6 km/h) = 4.3 METs
- Reasonable (3.6 to 4.4 mph/5.8 to 7.1 km/h) = 5.3 METs
- Quick (4.5 to five.0 mph/7.2 to eight km/h) = 8.5 METs
How Many Steps a Day to Lose Weight? Calculator Outcomes Defined
There’s no single “proper” variety of steps to take every day for weight reduction—it is dependent upon your weight-reduction plan and general exercise degree. As an alternative of fixating on a particular step depend, deal with how strolling matches into your broader weight reduction technique.
To drop extra pounds, you might want to eat fewer energy than your physique burns on daily basis (also called a “calorie deficit”).
To do that, use the Legion Calorie Calculator to estimate your whole every day power expenditure (TDEE)—the variety of energy you burn every day primarily based in your intercourse, weight, peak, age, and exercise degree.
When choosing your exercise degree, issue within the time you spend strolling utilizing your outcomes from the Legion Steps to Energy Calculator.
Then eat 20-to-25% fewer energy than your TDEE. Research exhibits this can be a good goal for shedding fats rapidly with out sacrificing muscle or wrestling with extreme starvation, lethargy, and the opposite hobgoblins of low-calorie weight-reduction plan.
And it doesn’t simply work within the lab—it really works in the true world, too. Listed below are a number of the shoppers from my body transformation coaching program. They adopted this recommendation and listed below are their outcomes:
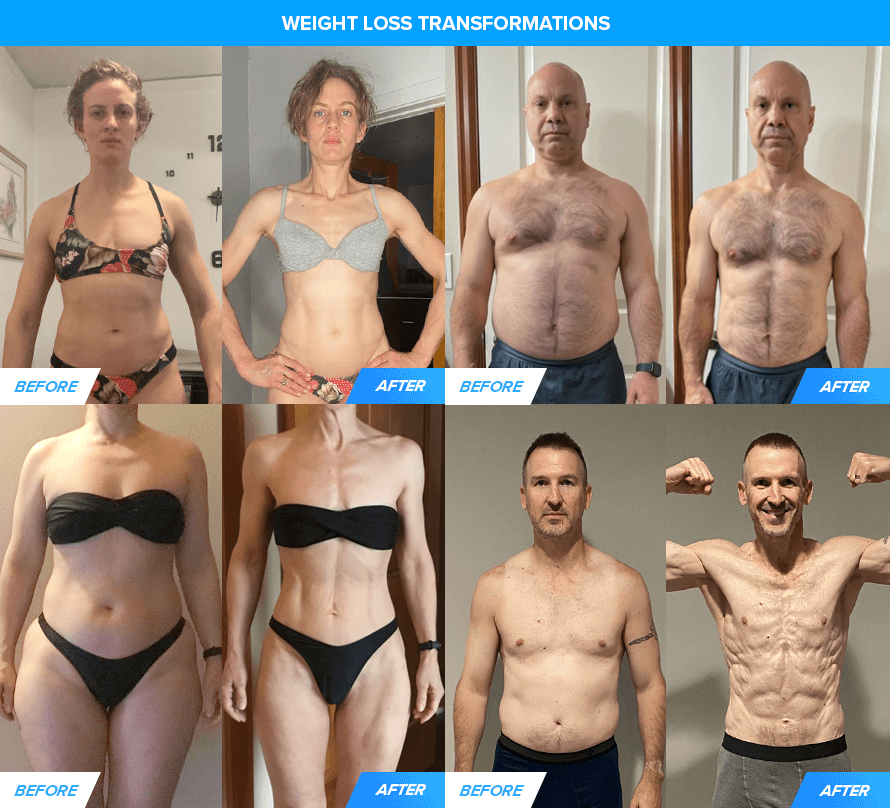
READ MORE: The Complete Guide to Safely and Healthily Losing Weight Fast
How Many Energy Does 10,000 Steps Burn?
Strolling 10,000 steps burns about 300-to-500 energy for most individuals—far fewer than many anticipate.
As an example, you possibly can simply eat again the energy you burn doing a ten,000-step stroll in a single small, wholesome snack—a handful of nuts, a yogurt, and a banana would do the trick.
Due to the hype round strolling 10,000 steps per day, many consider it’s a “candy spot” for fats loss and form their routines round hitting it.
However whereas strolling 10,000 steps benefits general well being and burns a good variety of energy, it doesn’t assure weight reduction.
To drop extra pounds, you need to burn extra energy than you devour. Strolling may also help you obtain that, however if you happen to don’t alter your calorie consumption, you’ll battle to see outcomes.
To study precisely the best way to weight-reduction plan to drop extra pounds, together with what number of energy, how a lot of every macronutrient, and which meals it is best to eat to achieve your well being and health objectives, take the Legion Diet Quiz. In lower than a minute, you’ll know precisely what weight-reduction plan is best for you. Click here to check it out.
Oh, and if you happen to ever wish to know what number of energy you’d burn taking a particular variety of steps, simply enter your particulars into the Legion Steps to Energy Calculator and enter that step depend within the “Variety of Steps” area.
For instance, if you wish to know “what number of energy does 6,000 steps burn?”, enter your particulars, enter 6,000 steps within the “Variety of Steps” area, and the calculator gives you your reply.
READ MORE: Do You Need to Walk 10,000 Steps a Day to Be Healthy?
The Advantages of Strolling
Strolling significantly reduces the danger of bodily illness, psychological decline, and even dying.
As an example, a meta-analysis printed within the journal Sport Medication (Auckland, N.Z.) examined seven research with 28,141 contributors and located that for each 1,000 steps folks took on daily basis, the danger of dying from all causes dropped by about 12%.
When evaluating folks with the very best and lowest every day step counts, researchers discovered that strolling 16,000 steps per day was linked to a 66% decrease threat of dying from all causes in comparison with strolling simply 2,700 steps per day.
FAQ #1: What number of energy does 20,000 steps burn?
Strolling 20,000 steps burns 600-to-1,000 energy for most individuals.
When you ever wish to know what number of energy you’d burn taking a particular variety of steps, simply enter your particulars into the Legion Steps to Energy Calculator and enter that step depend within the “Variety of Steps” area.
For instance, to learn how many energy 20,000 steps burn, enter your particulars into the calculator, enter 20,000 steps within the “Variety of Steps” area, and the calculator gives you your reply.
FAQ #2: What’s the typical energy per step burned whereas strolling?
The variety of energy burned per step varies extensively primarily based on peak, weight, and strolling velocity.
That stated, the typical US male is 5’9” and weighs 200 kilos. If he walks at a reasonable tempo, he burns roughly 0.053 energy per step.
For the typical US feminine—5’4”, 170 kilos—the quantity is round 0.042 energy per step on the similar tempo.
FAQ #3: What number of steps does it take to burn 500 energy?
It is dependent upon your peak, weight, and tempo, however the common female and male burn 500 energy in round 10,000 and 12,000 steps, respectively.
FAQ #4: Does strolling in place burn energy?
Sure, strolling in place burns energy—and greater than you may anticipate.
Research printed in Medication and Science in Sports activities and Train discovered that stepping in place burns virtually as many energy as strolling at 3 miles per hour on a treadmill—about 260 energy per hour versus about 300 energy.
Within the examine, individuals who stepped in place throughout TV commercials racked up ~2,100 steps and 25 minutes of motion in simply an hour of watching TV.
So whereas strolling in place gained’t match the calorie burn of a brisk out of doors stroll, it’s a simple technique to keep energetic, enhance power expenditure, and break up lengthy intervals of sitting—with out leaving your front room.
FAQ #5: What number of energy burned strolling 18 holes?
The typical golf course is 6,500 yards lengthy. Assuming you’re enjoying on a median course and strolling at a reasonable tempo, strolling 18 holes burns round 430 energy for the typical 5’9”, 200-pound male and 370 energy for the typical 5’4”, 170-pound feminine.
Which means the variety of energy burned strolling 9 holes is round 215 for males and 185 for girls.
In fact, these numbers are simply tough estimates. The precise variety of energy you burn strolling 18 or 9 holes of golf differ relying on physique weight, strolling velocity, terrain, and whether or not you’re carrying a bag, pushing a cart, or utilizing a caddy.
FAQ #6: Does strolling in heels burn extra energy?
Probably not. Strolling in heels might take extra effort due to the instability and the way they modify your biomechanics, which could improve what number of energy you burn. Nevertheless, the distinction is simply too small to matter, particularly in comparison with components like velocity and distance.
If you wish to burn extra energy whereas strolling, take into consideration strolling sooner and farther—not your footwear.
Scientific References +
- Murray, M. P., et al. “WALKING PATTERNS of NORMAL MEN.” The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume, vol. 46, 1 Mar. 1964, pp. 335–360, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14129683/.
- Murray, M. P., et al. “Walking Patterns of Normal Women.” Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, vol. 51, no. 11, 1 Nov. 1970, pp. 637–650, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/5501933/.
- Herrmann, Stephen D., et al. “2024 Adult Compendium of Physical Activities: A Third Update of the Energy Costs of Human Activities.” Journal of Sport and Health Science, vol. 13, no. 1, 1 Jan. 2024, pp. 6–12, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095254623001084, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jshs.2023.10.010. Accessed 26 Jan. 2024.
- Huovinen, Heikki T., et al. “Body Composition and Power Performance Improved after Weight Reduction in Male Athletes without Hampering Hormonal Balance.” Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, vol. 29, no. 1, Jan. 2015, pp. 29–36, https://doi.org/10.1519/jsc.0000000000000619.
- Tudor-Locke, Catrine, et al. “How Many Steps/Day Are Enough? For Adults.” International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, vol. 8, no. 1, 28 July 2011, p. 79, ijbnpa.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1479-5868-8-79, https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5868-8-79.
- Ungvari, Zoltan, et al. “The Multifaceted Benefits of Walking for Healthy Aging: From Blue Zones to Molecular Mechanisms.” GeroScience, vol. 45, no. 6, 26 July 2023, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-023-00873-8.
- The Health Benefits of Walking.
- Jayedi, Ahmad, et al. “Daily Step Count and All-Cause Mortality: A Dose–Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies.” Sports Medicine, vol. 52, 21 Aug. 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-021-01536-4.
- STEEVES, JEREMY A., et al. “Energy Cost of Stepping in Place While Watching Television Commercials.” Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, vol. 44, no. 2, Feb. 2012, pp. 330–335, https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0b013e31822d797e. Accessed 24 Mar. 2021.
